Miscarriage is a type of pregnancy loss that occurs before 20 weeks of gestation. Pregnancy loss is a broader term that includes miscarriages and other types of losses such as stillbirth and ectopic pregnancies.
Understanding the challenges and complexities surrounding pregnancy is crucial for expectant parents. Miscarriage and pregnancy loss are emotionally taxing events that bring about a lot of confusion and grief. It’s important to differentiate between the terms to provide clarity and appropriate support to those affected.
Miscarriage specifically refers to the spontaneous loss of a fetus before the 20th week of pregnancy, a common occurrence affecting many pregnancies. On the other hand, pregnancy loss encompasses a wider range of fetal losses, including miscarriage, stillbirth (loss after 20 weeks), and ectopic pregnancy (when an embryo implants outside the uterus). By educating ourselves on these terms, we create a more informed and supportive environment for those experiencing these difficult situations.

Credit: www.bannerhealth.com
Defining Miscarriage And Pregnancy Loss
The terms miscarriage and pregnancy loss often cause confusion. Both refer to the unfortunate event where a pregnancy ends on its own. Understanding their differences is key to providing support and knowledge to those affected. In the following sections, we’ll explore the meaning and distinguishing factors between these two terms.
Terms And Medical Meanings
Let’s clarify these often-interchanged terms:
- Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week.
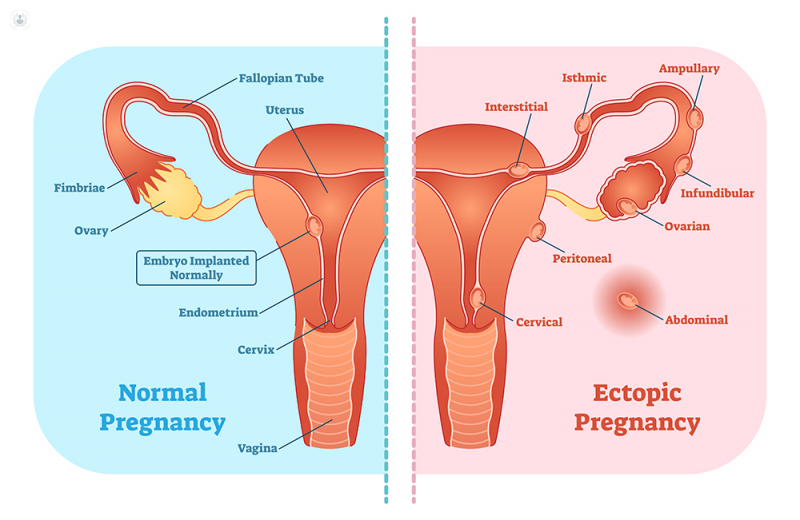
- Pregnancy loss is a broader term. It includes miscarriages and other types of loss like ectopic and molar pregnancies.
Distinctive Features
While miscarriage is a type of pregnancy loss, not all pregnancy losses are miscarriages. Other forms of pregnancy loss have unique signs and medical protocols.
| Type of Loss | Definition | When It Occurs |
|---|---|---|
| Miscarriage | Spontaneous pregnancy loss | Before the 20th week |
| Stillbirth | Pregnancy loss after the 20th week | After the 20th week |
| Ectopic Pregnancy | Fertilized egg implants outside uterus | Early in pregnancy |
| Molar Pregnancy | Abnormal tissue growth in the womb | Early in pregnancy |
Recognizing the differences between miscarriage and pregnancy loss provides clarity. It helps in understanding the experiences of those going through such difficult times. Each type of loss has its unique journey and requires distinct forms of care and support.
Common Myths About Miscarriage
Miscarriages are traumatic and often misunderstood. People have many beliefs about them. Some beliefs are not true. This confusion adds more pain to those affected. Let’s expose the myths and uncover the facts. Doing so can help in healing and understanding this difficult experience.
Myth Versus Fact
Many believe myths about miscarriage. They think certain acts or situations cause it. That’s not always true. Here are some widely held myths and the truth behind them.
- Myth: Lifting heavy objects causes miscarriage.
- Fact: Miscarriages are typically due to genetic issues, not physical strain.
- Myth: Miscarriages are rare.
- Fact: Up to 20% of known pregnancies end in miscarriage.
- Myth: A stressful event can lead to miscarriage.
- Fact: Normal stress doesn’t cause miscarriage; however, severe stress may be a factor.
Causes And Blame
Understanding why miscarriages happen can prevent false blame. It’s important to know the common causes. This helps support those going through it.
| Causes of Miscarriage | Blame or No Blame? |
|---|---|
| Chromosomal abnormalities | No blame |
| Lifestyle factors (smoking, drugs) | Some blame, but support and understanding are needed |
| Untreated health issues | No blame, emphasizes the need for health care |
| Environmental toxins | No blame, but raises awareness for safer environments |
It’s critical not to blame oneself or others for a miscarriage. Many factors are beyond control. Support and accurate information are key.
Understanding Pregnancy Loss
Pregnancy loss represents a deep and personal experience. It occurs when a pregnancy does not continue. It can happen early or late in gestation. Many terms describe this heart-rending occurrence. They often interchangeably use the word miscarriage. Pregnancy loss encompasses all forms of an unborn baby’s passing prior to 20 weeks’ gestation.
Types Of Pregnancy Loss
Various forms of pregnancy loss exist. Each type originates from unique reasons. They have different implications for future pregnancies.
- Chemical Pregnancy: This is loss soon after implantation.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An embryo grows outside the uterus.
- Molar Pregnancy: A nonviable egg implants and grows abnormally.
- Missed Miscarriage: The fetus stops developing but the body does not recognize the loss immediately.
Emotional Impact
The emotional aftermath of pregnancy loss carries significant weight. Parents may feel a range of emotions from sadness and grief to confusion and anger.
Grief Counseling: Seek professional help if necessary.
Support Groups: Connecting with others who have experienced similar losses can provide comfort and understanding.
Remember, healing takes time. Each person’s journey through loss is unique.
Risk Factors And Prevention
Understanding the risk factors and preventive strategies can offer insight into the difference between miscarriage and pregnancy loss. Identifying risks associated with pregnancy can inform expectant mothers and families on how to better safeguard maternal health and improve pregnancy outcomes. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Identifying Risks
Several factors may increase the risk of miscarriage or pregnancy loss. Some of these risks include:
- Age: Women over 35 have a higher risk.
- Previous miscarriages: Past occurrences can indicate future risks.
- Chronic conditions: Health issues like diabetes or hypertension play a role.
- Uterine or cervical issues: Abnormalities can affect pregnancy.
- Lifestyle habits: Smoking, excessive caffeine, and alcohol use are risk factors.
Potential Preventative Measures
To minimize the chance of miscarriage, certain preventative measures can be effective:
| Preventive Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular prenatal care | Monitoring health can catch issues early. |
| Maintain a healthy diet | Nutrition supports fetus growth. |
| Manage health conditions | Keeping blood sugar and blood pressure under control is key. |
| Avoid harmful substances | Eliminate alcohol, tobacco, and non-prescribed drugs. |
| Limit caffeine intake | Less caffeine is better for baby’s development. |
Coping With Grief
Experiencing a miscarriage or pregnancy loss is a profound and personal sorrow. Many parents feel a deep sense of loss and grief. It is crucial to remember that these feelings are normal and individual paths to healing vary. The process of coping with grief requires patience, self-compassion, and support.
Seeking Support
Reaching out to others can be a lifeline during this tough time. Friends, family, and professionals offer necessary emotional support.
- Counseling: A therapist specializes in grief can help parents process emotions.
- Support Groups: Sharing with parents who have experienced a similar loss is comforting.
- Community Resources: Local health services often provide programs to assist grieving families.
Mourning And Moving Forward
Grieving is a personal journey with no set timeline. Accepting loss is a gradual process that allows healing.
- Recognize the significance of the loss and allow yourself to feel the sorrow.
- Engage in memorial rituals that hold personal meaning.
- Embrace positive coping mechanisms like journaling or creative activities.
- When ready, consider the future with hope and self-care.

Credit: www.hourglassomnimedia.com
Medical And Emotional Support
The journey through pregnancy can be filled with tremendous joy. Sadly, some face the heartache of pregnancy loss or miscarriage. During these tough times, both medical and emotional support are crucial. They provide the care needed for healing and recovery.
Healthcare Assistance
After a pregnancy loss, top-notch healthcare is vital. Doctors and nurses help the body heal. They check for any health issues. They also make sure the body is recovering properly. A healthcare team can offer:
- Physical evaluations to ensure health is on track.
- Medication if needed, to aid in the healing process.
- Follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
Psychological Therapies
The pain of losing a pregnancy is deep. Emotional healing is just as important as physical healing. Therapists and counselors provide a safe space to grieve. They offer strategies to cope with the loss. Support groups connect people with others who understand. This care includes:
- Counseling sessions for personal emotional support.
- Couples therapy to help partners navigate grief together.
- Support groups for sharing experiences with those in similar situations.

Credit: www.pacehospital.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Difference Between Miscarriage And Pregnancy Loss
What Causes A Miscarriage?
A miscarriage is often caused by chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus, but can also result from medical conditions, hormonal issues, and lifestyle factors. Environmental and genetic factors also play a role.
Can Miscarriage Be Prevented?
In many cases, miscarriage can’t be prevented because it often occurs due to genetic abnormalities. However, avoiding risk factors like smoking, alcohol, and ensuring proper prenatal care may reduce the risk.
What Are Signs Of Pregnancy Loss?
Signs of pregnancy loss include heavy bleeding, cramping, and abdominal pain. Other symptoms can be the loss of pregnancy symptoms, and no fetal movement or heartbeat detected by an ultrasound.
How Is Miscarriage Different From Stillbirth?
Miscarriage typically occurs before 20 weeks of gestation, while stillbirth generally refers to the loss of a fetus after 20 weeks. Both result in the loss of pregnancy but occur at different stages.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances between miscarriage and pregnancy loss is crucial for emotional healing and medical insight. These terms encompass different experiences, each with a unique impact on expectant parents. By educating ourselves, we foster empathy and provide better support to those grappling with such profound losses.
Remember, seeking help and conversation is a powerful step toward recovery.