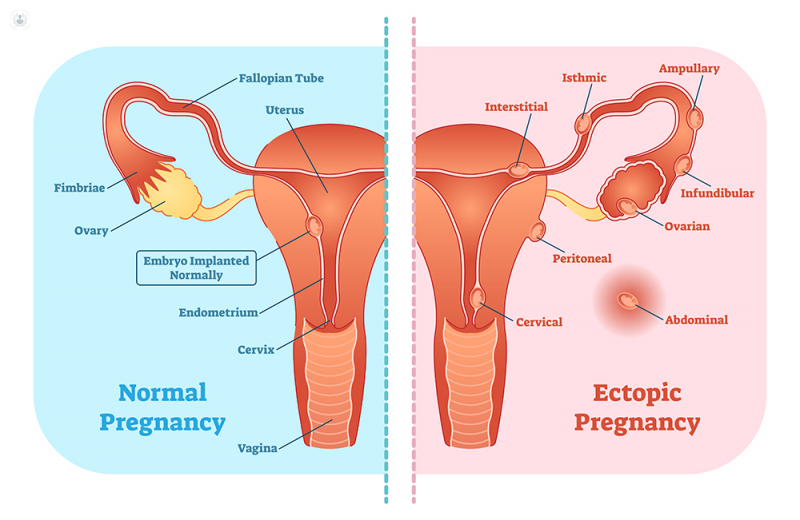
A miscarriage is the loss of a pregnancy within the womb up to 20 weeks, while an ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, most often in a fallopian tube. These two conditions differ in location and potential outcomes for the mother. Miscarriage vs. Ectopic Pregnancy.
Understanding the differences between miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy is crucial for anyone concerned about the potential risks in early pregnancy. Miscarriage is relatively common, affecting about 10-20% of known pregnancies, and usually doesn’t pose a long-term risk to the mother’s health.
On the other hand, an ectopic pregnancy is less common, occurring in about 1-2% of pregnancies, but can lead to serious complications if not treated promptly, including life-threatening internal bleeding. Recognizing the symptoms, which can range from mild cramping to severe abdominal pain, and seeking immediate medical attention can help manage these conditions effectively. Medical professionals typically diagnose these conditions through ultrasound and blood tests, providing appropriate care based on the specific situation.

Credit: www.intechopen.com
Defining Miscarriage And Ectopic Pregnancy
Understanding the complexities of pregnancy goes beyond the joy of expecting a new life. It involves knowledge about potential complications, such as miscarriages and ectopic pregnancies. These terms often cause confusion and distress. It is crucial to define them clearly.
Characteristics Of Miscarriage
A miscarriage, known medically as a spontaneous abortion, occurs when a pregnancy ends on its own within the first 20 weeks. This loss of pregnancy has several key characteristics:
- Bleeding: The most common sign, varying from light spotting to heavy bleeding.
- Cramping: Abdominal or pelvic pain, often more severe than menstrual cramps.
- Passing tissue or clots: Women might expel tissue or clots from the vagina.
It’s important to seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.
Nature Of Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy differs as it develops outside the uterus, commonly in a fallopian tube. It cannot proceed normally and requires immediate care.
- Location: Ectopic pregnancies implant in non-uterine tissue.
- Symptoms: Sharp, stabbing pains on one side of the abdomen, spotting, and at times dizziness.
- Risks: If untreated, it can cause the fallopian tube to burst, leading to serious complications.
Understanding and recognizing the differences between these conditions is vital to maternal health and well-being.

Credit: pubs.rsna.org
Causes Behind The Conditions
Exploring the ‘Causes Behind the Conditions’ brings into focus the health intricacies women face with miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy. Understanding these causes is vital. Let’s delve into the specifics.
Factors Leading To Miscarriage
A miscarriage is a loss of pregnancy during the first 20 weeks. Many factors can lead to this unfortunate event. Here are some key causes:
- Chromosomal abnormalities often lead to developmental issues with the fetus.
- Hormonal imbalances impact the body’s ability to maintain a pregnancy.
- Infections can disrupt the healthy progression of pregnancy.
- Certain medical conditions in the mother, such as uncontrolled diabetes or thyroid disease, affect pregnancy health.
- Lifestyle factors like smoking, excessive caffeine, and alcohol intake can also be culprits.
Triggers For Ectopic Pregnancies
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus. These triggers are responsible:
- Inflammatory diseases, such as pelvic inflammatory disease, often cause ectopic pregnancies.
- History of ectopic pregnancies or pelvic surgeries can increase risk.
- Abnormalities in fallopian tube structure can prevent the egg from reaching the uterus.
- Hormonal factors and certain fertility treatments also play a role.
- A history of sexually transmitted infections, like gonorrhea or chlamydia, might damage the reproductive system.
Identifying The Symptoms
Understanding the difference between miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy is crucial. Both conditions involve significant emotional and physical challenges. Knowledge of their symptoms empowers women to seek timely medical attention. This section highlights the key symptoms associated with each condition.
Recognizing Miscarriage SignsRecognizing Miscarriage Signs
Miscarriage, often referred to as a spontaneous abortion, involves the loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week.
- Vaginal bleeding: This can range from light spotting to heavier bleeding with clots.
- Lower abdominal pain or cramping: Pain may be persistent or intermittent.
- Back pain: Particularly in the lower back, which can vary in intensity.
- Loss of pregnancy symptoms: Such as nausea and breast tenderness.
Detecting Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in a fallopian tube.
- Sharp or stabbing pain: Usually felt on one side of the abdomen or pelvis.
- Vaginal bleeding: Unlike the menstrual period, it is often lighter and darker in color.
- Shoulder pain or neck pain: This occurs if blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy builds up under the diaphragm.
- Dizziness or fainting: It’s a sign of internal bleeding and requires immediate medical attention.
Medical Diagnosis And Procedures
Understanding the difference between a miscarriage and an ectopic pregnancy is crucial. Medical professionals use specific diagnosis methods and procedures to identify each condition accurately. Getting a correct diagnosis is vital for the appropriate medical treatment and emotional support needed during such challenging times.
Diagnosing a MiscarriageDiagnosing A Miscarriage
Miscarriages usually occur within the first 20 weeks of pregnancy. To diagnose a miscarriage, doctors may use several methods:
- Physical exam: To check for any complications or signs of a miscarriage.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to view the uterus and confirm a heartbeat.
- Blood tests: To measure hormone levels, such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
- Pelvic exam: To determine if the cervix has started to dilate.
Confirming An Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when an embryo implants outside the uterus. It requires immediate medical attention. Here’s how doctors confirm an ectopic pregnancy:
- Pelvic exam: To identify any pain or mass in the fallopian tubes or ovary.
- Ultrasound: To locate the exact position of the pregnancy.
- Blood tests: To track hCG levels, as they often rise slower than in a normal pregnancy.
- Laparoscopy: As a surgical procedure, it allows doctors to directly look at the fallopian tubes to find the ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment Options And Recovery
The journey to recovery after a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy can be challenging. It involves both physical healing and often emotional recovery. The medical approach to treating these conditions varies, but understanding the options helps in navigating this difficult path. Let’s explore the most common treatments and what to expect during the recovery process.
Treating A Miscarriage
Miscarriages often start naturally without the need for medical intervention. This process is called expectant management. However, if it doesn’t start on its own or if it’s incomplete, with some pregnancy tissue remaining in the uterus, doctors may suggest other treatments:
- Medication: Drugs like misoprostol may help complete the process.
- Dilation and curettage (D&C): A surgical procedure to remove pregnancy tissue.
Recovery involves physical rest and monitoring for complications. Light bleeding and cramps may occur.
Managing An Ectopic Pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy requires prompt treatment to prevent severe complications. The treatment options include:
- Medication: Methotrexate can stop the growth of the embryo.
- Surgery: Laparoscopy removes the ectopic tissue and repairs any damage.
Post-treatment, hormone levels are monitored until they return to pre-pregnancy levels. Rest and avoiding strenuous activity are crucial for recovery.
Support from healthcare providers, counselors, and support groups help in emotional recovery.

Credit: www.journeyforjasmine.com
Emotional Impact And Support
Navigating the emotional landscape after experiencing a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy can be overwhelming. Both events involve the loss of a pregnancy, but each has unique challenges and requires specific ways to process the grief and seek support. Recognizing the needs of individuals going through either can provide comfort and help them find a pathway to healing.
Coping With Grief After Miscarriage
Grief from a miscarriage is profound and can touch every aspect of life. Feelings of sadness, loss, and confusion are common reactions. Allow yourself to mourn and acknowledge the pain as a step toward recovery.
- Seek comfort in friends and family.
- Participate in memorial rituals to give tangible form to your loss.
- Consider joining a support group to connect with others who understand.
- Consult mental health professionals if the burden becomes too heavy to carry alone.
- Express your feelings through journals or art, which can be therapeutic outlets.
Support Systems For Ectopic Pregnancy Loss
An ectopic pregnancy loss adds layers of physical risks to the emotional toll. Accessing medical and emotional support as soon as possible is crucial for health and well-being.
- Maintain regular medical follow-ups to ensure physical healing.
- Lean on close relationships for emotional sustenance and practical aid.
- Explore online forums or local health centers for specialized support groups.
- Professional counseling can help address complex emotions and promote resilience.
- Engage in self-care practices, such as mindfulness or gentle exercise.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is The Difference Between Miscarriage And Ectopic Pregnancy
What Causes A Miscarriage?
A miscarriage is often caused by chromosomal anomalies in the fetus, hormonal issues, maternal health conditions, or maternal age. It typically results from natural, unpreventable factors affecting fetal development early in pregnancy.
How Is An Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
An ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed through a combination of pelvic examinations, ultrasounds, and blood tests that measure hCG levels. These help determine if the embryo is outside the uterus.
Can One Survive An Ectopic Pregnancy?
Survival and recovery are possible with prompt treatment. Ectopic pregnancies require medical intervention, as the growing embryo can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated.
What Are The Symptoms Of Miscarriage?
Miscarriage symptoms include vaginal bleeding, cramping, pain in the abdomen or lower back, and passing of tissue or fluid from the vagina. Any suspected miscarriage should prompt immediate medical consultation.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between a miscarriage and an ectopic pregnancy is crucial for proper medical care and emotional support. Both situations require immediate attention from healthcare professionals. As we’ve explored their differences, remember that each woman’s experience is unique. Seeking guidance from a doctor can provide clarity and the necessary steps for healing and future planning.
Stay informed and prioritize your health for the best outcomes.